Module A2 – Wonders of wood
Wood has had a big impact on the scientific revolution, which started in Europe in the 16th century. People used paper as their main instrument for developing and sharing ideas. The industrial manufacturing of paper from wood accelerated rapidly in the 1800s, enabling a sharp increase in the exchange of printed information.
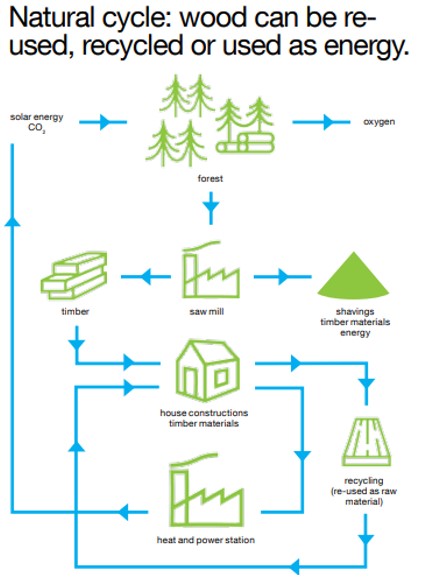
Wood is a versatile, renewable, and fully recyclable natural material (Figure 1.)with various uses, and it has always satisfied people’s diverse and ever-changing needs. Forests are one of our planet’s most important natural resources. Throughout history, forests have provided protection and a wide variety of goods such as food, building material and raw material for the industrial sector to use. Roughly three quarters of land area on Earth is covered by forests. More wood grows annually than is currently used.
Different parts of a tree are used for purposes that produce the highest added value. Logs are mainly made from (lower parts of) large-diameter stems and, in turn, these are used to make wood products, such as timber and plywood for construction. Thinner trees and treetops are used as pulpwood, which is used to make pulp, paper, board and other bioproducts. Bark and branches are used to generate renewable energy.

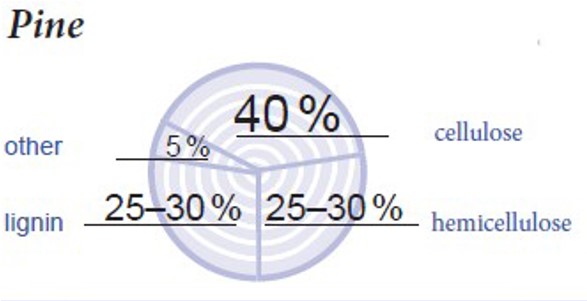
Wood is primarily composed of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin. Wood also contains minor amounts of extractives such as pitch, resins and inorganic matter. The composition varies according to the tree species. The composition of a pine wood can be seen in Figure 1.
Every compound available from trees can be recovered at pulp mills in the context of pulp production. Future bio-refineries will use wood in increasingly versatile ways, as the raw material for a growing number of different products.
A major part of the value of wood is its use in production of engineered wood products. These applications include several sawmilling and wood-based panel products, such as sawn timber, plywood, LVL, chipboard and various panels. Together with other renewable wood-based solutions, engineered wood products have an increasing importance in global climate change mitigation due to their ability to sequester carbon dioxide to make biomass.
Wood from commercial forests is utilised in products that meet our daily needs, with the goal of reducing the reliance on and replacing non-renewable resources. Sustainable forestry combines three key goals:
- preserving nature’s ecological carrying capacity
- safeguarding social and cultural values associated with forests
- maintaining financial viability for all stakeholders.
These principles ensure that our forests continue to provide ecologically, socially and economically sustainable wood raw materials.
All in all, wood has many different benefits as a raw material. In addition to being both sustainable and renewable it provides good technical properties such as insulation, strength, and durability. Therefore, wood is a highly valuable and renewable resource for a sustainable bioeconomy.
