Module A4 – Wood products
Introduction
There are a lot of versatile wood products panels and timbers of which the naming is based on either the production method and/or the type of the raw materials (wood species) or the form of the raw materials (e.g., chips, flakes, veneer, fibreboard, timber). Wood products are mainly manufactured from the trunk of the tree.
In this module, you will get a general insight into the woodworking industry, learn the raw material sources of the woodworking industry, gain knowledge about the properties of wood products and, lastly, you will increase your knowledge about end uses.
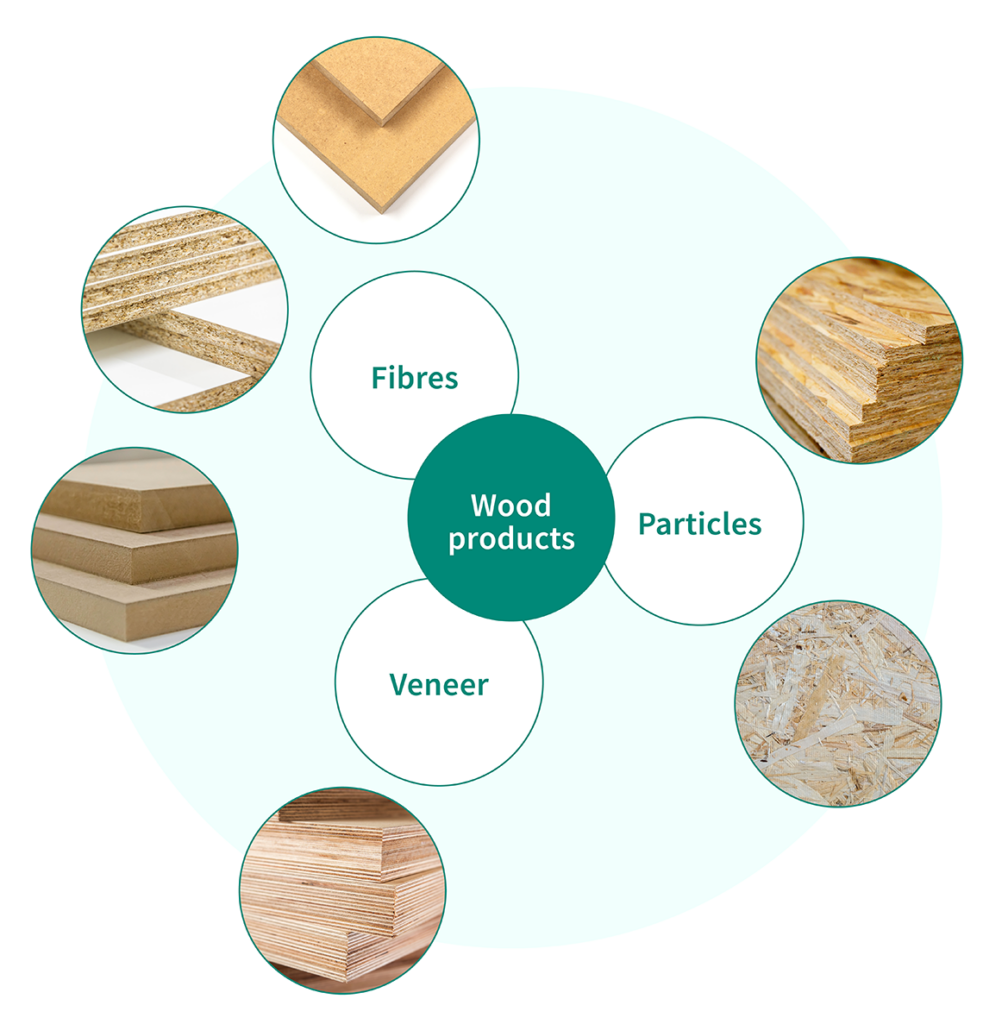
Wood-based panels and timber
Plywood
Plywood is a strong and stiff wooden panel made by gluing together veneers that are made by peeling wood logs into 1.5-3.0 mm sheets. Standard plywood is produced in two main categories based on the used raw material, softwood (Figure 2a) and birch (Figure 2b) plywood.

Laminated veneer lumber (LVL)
Laminated veneer lumber (LVL) is a versatile material and can be used in a multitude of applications, suitable for use both indoors and outdoors. Spruce and pine are common wood species used in LVL production. Different grades of LVL are produced to meet the standardized product specification and recommendation. Click here if you want to read more about the basic properties of LVL.

Particleboard
Particleboard is made from particles, small wooden chips that are glued together in a drum after which the mix is transferred with a conveyor to forming belts and rolls. Finally, the particleboard is pressed at high temperature and pressure. Raw materials used are for example by-products from other wood panel plants and sawmills, round timber, and recycled wood.
Furniture and fixture manufacturing is the largest application for particleboards. Two-thirds of particleboard production is used in the furniture industry, followed by the construction sector, where particleboards are used in walls, floors, and doors.

Other wood-based panels
Engineered wood products
Hard and soft fibreboards
Both hardboard and softboard are engineered wood products, each of which have their own characteristics in terms of raw material, manufacturing, and requirements for use.

MDF – Medium Density Fibreboard
MDF is made from small wood, as well as chips and sawdust, the sawmill industry’s by-products, the raw materials mainly consisting of hardwood.
The furniture industry uses MDF in the manufacturing of sofas, armchairs, beds, and fixed furniture. MDF can be coated with a variety of materials and is well suited for production of components in the door and window industry
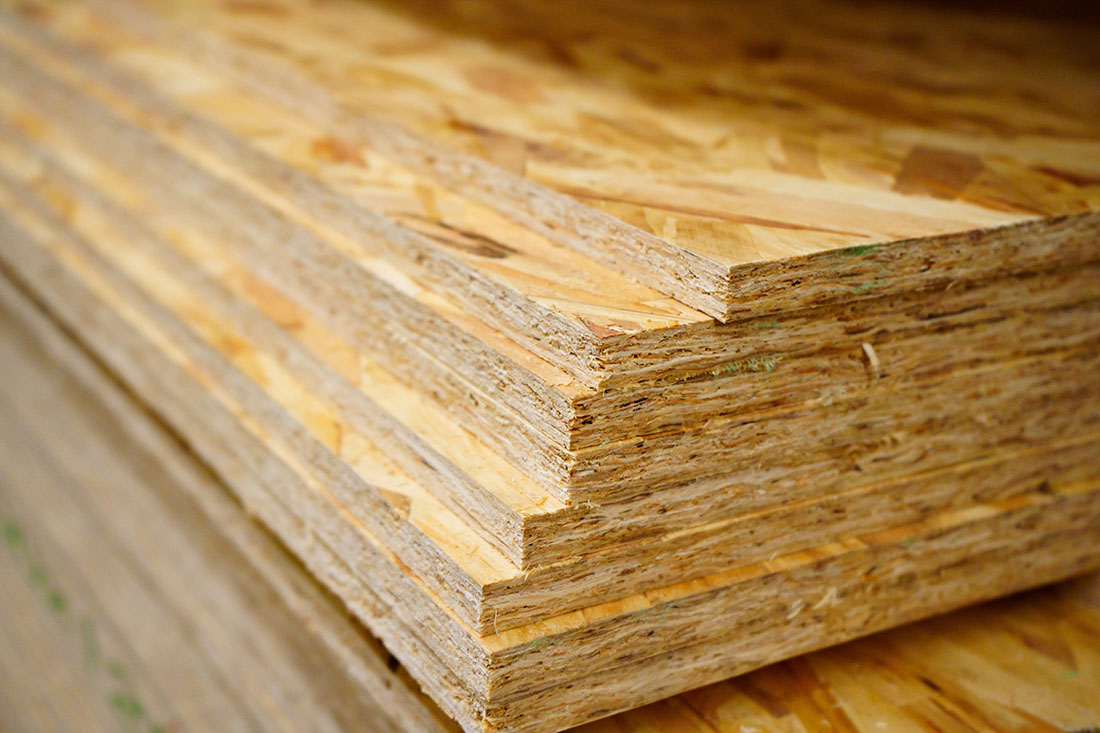
OSB – Oriented Strand Board
Oriented Strand Board (OSB) (Figure 6.) is made from parallel-oriented long wood strands, i.e., long, thin wood elements. OSB is mainly developed to be used for structural applications in construction. Its strength properties are similar to panel products made from veneers.


Parallel strand lumber (PSL)
Parallel strand lumber has a strong and stiff structure, and it does not twist or crack. Veneer strips give PSL a visually distinctive surface, which is often left visible. PSL is used in constructions as a load-bearing structure . It is also well suited for long spans.
Laminated strand lumber (LSL)
Laminated strand lumber is used to make beams that are used in construction in floors, walls, ceilings and roof trusses, and as different components, for example, in stair elements. It is made from small diameter softwood as a raw material. Unlike in particleboard manufacturing, the strands are made quite long, with a thickness-to-length ratio of 1:150

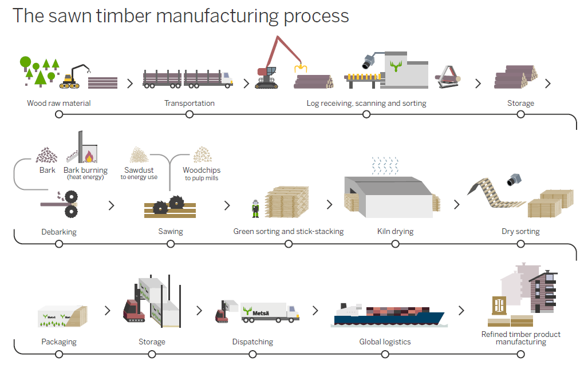
Sawn timber
Sawn timber comprises timber the surfaces of which have been sawn on four sides. Timber is also available without edging where only two sides have been sawn. Different profiles can also be made using special sawing methods. The logs are sawn to standard dimensions, i.e., thickness, width and length utilizing as much as possible of the available raw material. After cutting, the timber is graded and sorted according to certain quality specifications

It is light, strong, easy to process, and its visual appearance offers various opportunities. Sawn timber is mainly used in construction, both residential and commercial, wooden bridges, platforms, noise barriers, sport parks and playgrounds.
The further processing of sawmill industry products usually takes place at a sawmill or, according to the current trend, in companies specialising in further processing. The different processed products are e.g.:
- Planed and painted timber
- Finger-jointed timber and components
- Glulam beams and panels
- Cross-laminated timber, CLT
- Logs
- Structures with nail plates
- Thermally modified timber
- Impregnated timber
Glulam boards
Glulam boards are made from solid planed and cut timber by glueing the edges of timber pieces together to form a board. Glulam boards are used by the furniture and fixture industry to make shelves and desktops.
Glulam beams
GLT is made by glueing lamellas together. It is a strong, solid wood product designed for load-bearing structures and long spans). GLT has a maximum height of about two metres and a maximum length of around 30 metres. Primary applications include load bearing posts and beams in commercial, industrial, and agricultural construction and in public buildings, such as schools and sports facilities. GLT is also used in bridge building.
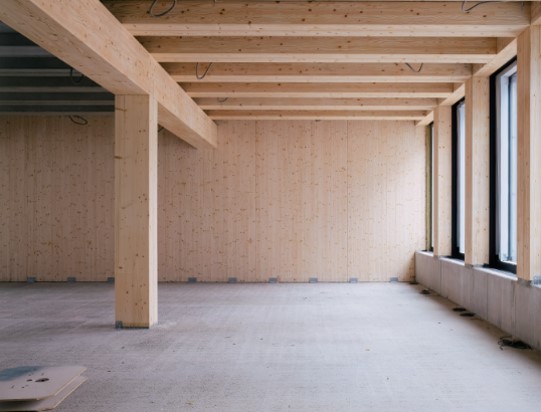


Cross-laminated timber panels
Cross-laminated timber (CLT) panels are solid wood panels made from timber layers glued together in a crosswise pattern. The panels can be used as load-bearing and stiffening structures in building walls and floors. It is possible to build entire exterior wall structures from CLT panels using single panels as combined load bearing, and insulation structures.
By-products of the sawmill industry
The sawing process produces various by-products that are financially significant for the sawmill industry. Wood chips, sawdust and bark all have their own uses. Sawn timber accounts for roughly 80 % of revenues, and the by-products for 20 %.
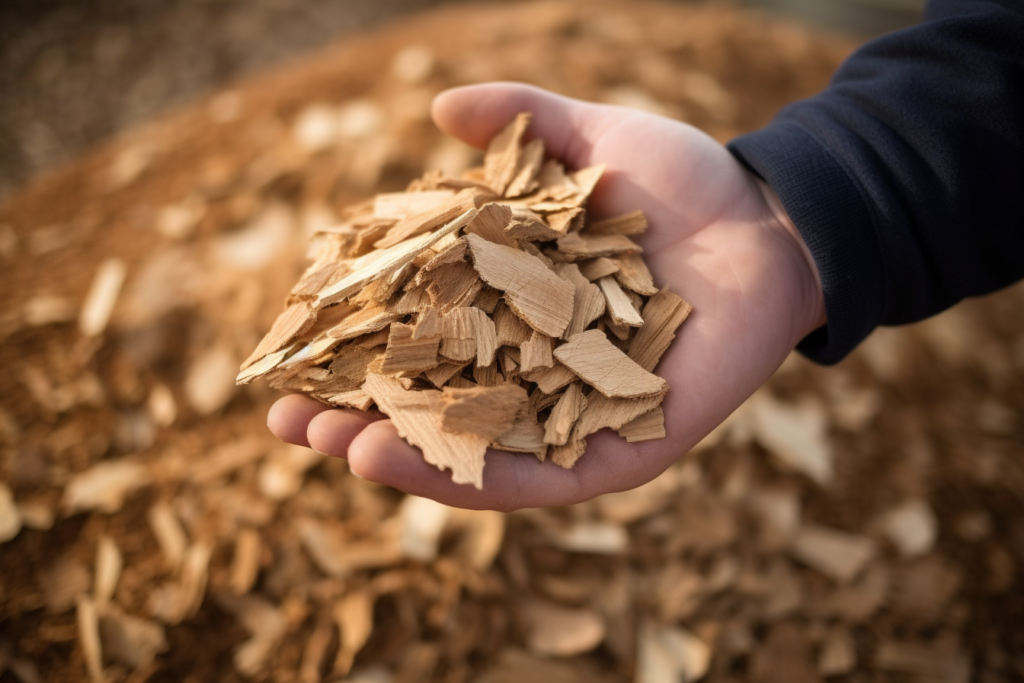

Wood chips produced from leftovers in the sawing process are pure and can directly be delivered as raw material for the pulp industry.
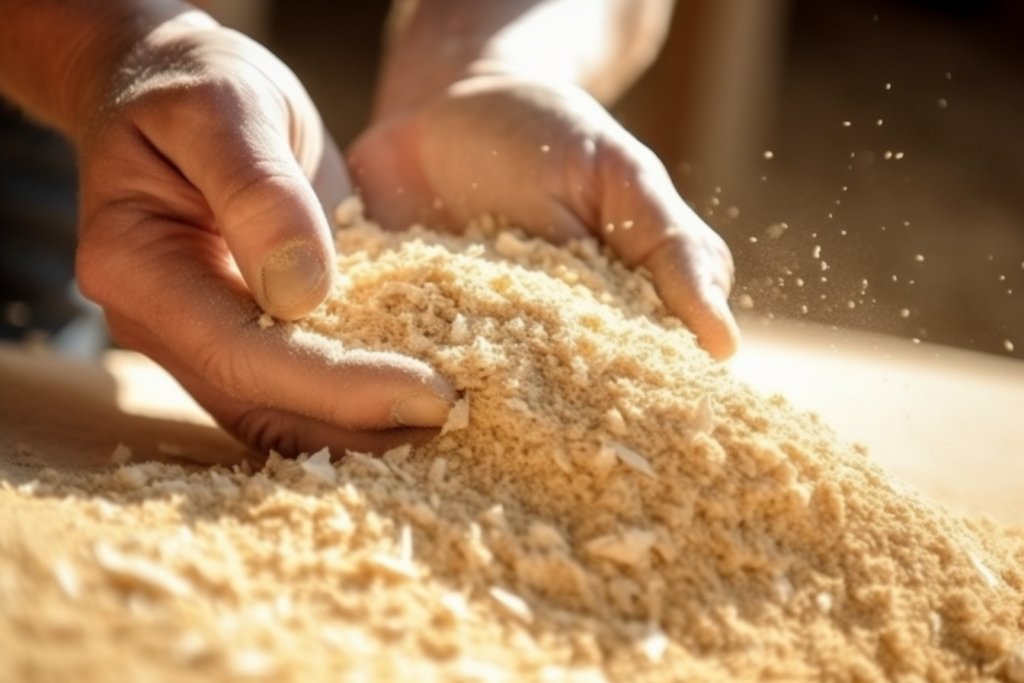

Saw dust used as fuel in thermal power plants, pulp manufacturing, the production of wooden pellets and as raw material in the particleboard and fibreboard industries.
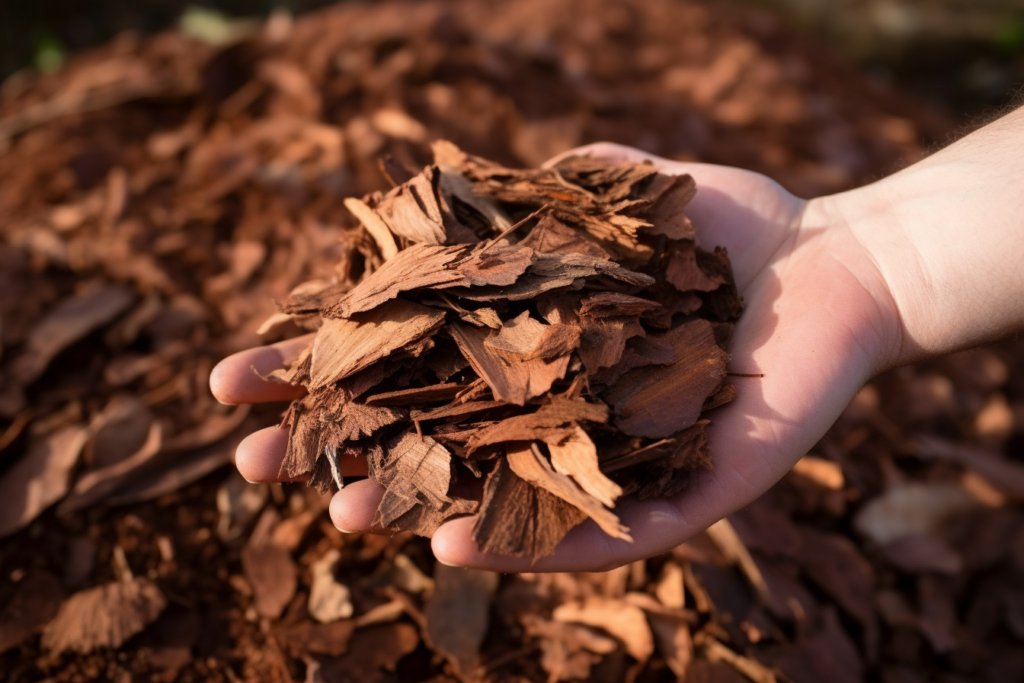

Bark is primarily used together with saw dust in thermal power plants at sawmills, also sold as fuel to industrial energy producers.
Innovative uses of by-products
Woodio
Woodio is a Finnish interior and design brand that makes products using their signature, innovative and sustainable Woodio material. Woodio material is world’s first 100% waterproof solid wood composite of wood chips and resin.

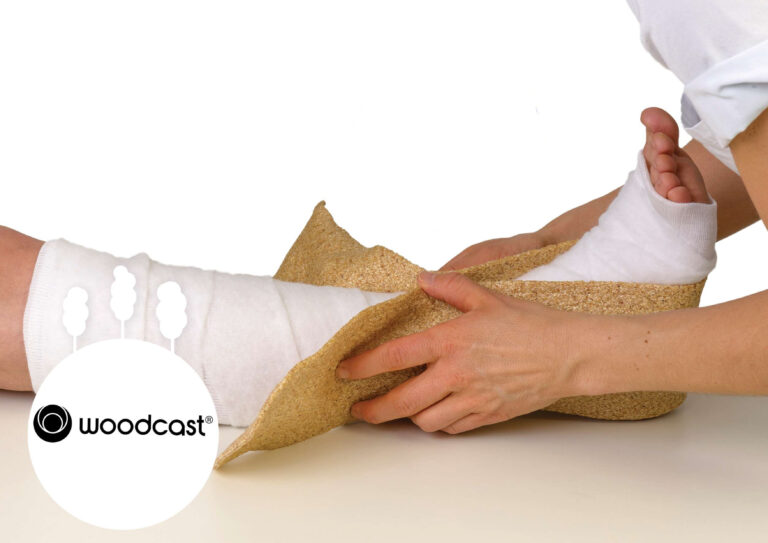
Woodcast
Woodcast is a wood composite which can replace all gypsum and synthetic plaster casts in hospitals. The material, made from aspen chips and biodegradable plastic, is light, durable and breathable. It is hard and durable in room temperature, but pliable and self-adhesive when warmed up.

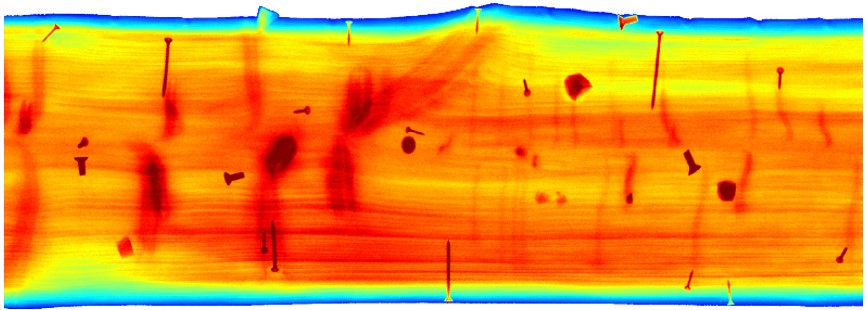
Visual quality and strength
Sawn materials are graded based on their visual quality and strength (Figure 18). Automated grading systems are based on machine vision. Scanners and cameras are used in sorting the products. In addition to the dimensions, cameras identify any knots, wane, discolouration, cracks, resin pockets and foreign objects and insect defects. The strength of sawn timber to be used in construction must be strength graded and is determined based upon grading rules. (Link: Strength grading of sawn timber – ForestBioFacts)